All content on this site is intended for healthcare professionals only. By acknowledging this message and accessing the information on this website you are confirming that you are a Healthcare Professional. If you are a patient or carer, please visit the MPN Advocates Network.
The mpn Hub website uses a third-party service provided by Google that dynamically translates web content. Translations are machine generated, so may not be an exact or complete translation, and the mpn Hub cannot guarantee the accuracy of translated content. The mpn and its employees will not be liable for any direct, indirect, or consequential damages (even if foreseeable) resulting from use of the Google Translate feature. For further support with Google Translate, visit Google Translate Help.
The MPN Hub is an independent medical education platform, sponsored by AOP Health, GSK, Sumitomo Pharma, and supported through educational grants from Bristol Myers Squibb and Incyte. Funders are allowed no direct influence on our content. The levels of sponsorship listed are reflective of the amount of funding given. View funders.
Now you can support HCPs in making informed decisions for their patients
Your contribution helps us continuously deliver expertly curated content to HCPs worldwide. You will also have the opportunity to make a content suggestion for consideration and receive updates on the impact contributions are making to our content.
Find out more
Create an account and access these new features:
Bookmark content to read later
Select your specific areas of interest
View MPN content recommended for you
Outcomes in patients with MPN-associated splanchnic vein thrombosis
Patients with myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPN) are at increased risk of splanchnic vein thrombosis (SVT), including thrombosis in the portal vein, splenic vein, mesenteric vein, or hepatic vein (Budd-Chiari syndrome).1 MPN-SVT is a rare condition with a significant mortality and morbidity burden in patients. While the clinical course appears to differ from MPN without SVT, its management poses specific challenges to clinicians and requires specialist management from hepatologists and hematologists. There is a lack of robust clinical data in this specific patient population.1
The UK Myeloproliferative Neoplasms Associated Splanchnic Vein Thrombosis (MASCOT) registry was a large, national, retrospective study of patients with MPN-SVT, and the findings were recently presented by Hargreaves, et al.1 at the European Hematology Association (EHA) 2022 Congress.1 We summarize the key findings below.
Method
The aim of the study was to establish a UK national web-based clinical registry of patients with MPN-SVT. The primary objectives were to determine the thrombosis recurrence rate, the death rate, and the cause of death. The secondary objectives included the demographic and clinical features, and the trends and variations within UK clinical practice.
The MASCOT registry received pseudo-anonymized data from nine large hematology/hepatology centers between 2019 and 2022. Current and historical cases were included, and demographic, radiologic, clinical, and outcome data were collected.
Results
- A total of 238 patients were registered in 33 months.
- 137 (57.6%) were female and 101 were male (p = 0.01).
- Age at diagnosis was lower in female patients.
- Median time from SVT diagnosis to registration was 8 years, 11 months (range, 11 days–44 years).
- Median follow-up time from SVT diagnosis was 7 years, 4 months (range, 35 days–31 years).
- The number of patients with MPN at registration was 213.
- Polycythemia vera (PV) was the most common subtype at 44%, followed by essential thrombocythemia (ET) at 19%, and MPN-unclassifiable (MPN-U) at 14%.
- In 209 patients, 96.7% had a JAK2 V617F mutation, and the remaining patients had a CALR mutation
- MPN diagnosis changed for 54 patients (25.4%) from time of diagnosis to time of registration in this study.
- Most commonly, this was a change from an isolated JAK2 V617F to PV (n = 11) or MPN-U (n = 4).
- ET diagnosis changed to post-ET myelofibrosis in 11 patients, and to PV in four patients.
- MPN-U diagnosis changed to PV in four patients.
Thrombotic events
Single and multiple vein thrombosis were recorded in 127 and 92 patients, respectively.
- The majority of single vein thrombosis cases were classified as portal vein (n = 57), followed by hepatic vein (n = 50), splenic (n = 15), and mesenteric (n = 5).
- In patients with multiple vein thrombosis, portomesenteric axis involvement was common.
Radiological outcomes were evaluated based on 12-month scans (n = 112), or the most recent imaging data (median, 2.1 years; n = 169). Outcomes, such as stable thrombosis, recanalization, or recurrence, were similar between these groups. Amongst patients with 12-month data, those with hepatic vein thrombosis were at slightly higher risk for extension compared with patients with non-hepatic vein thrombosis. However, the association between hepatic vein thrombosis and extension or recurrence at 1 year was statistically insignificant (p = 0.117).
Treatment strategies
Anticoagulation
The initial anticoagulation strategy was heparin in line with the local policy. Over half of all patients were treated with warfarin (52.5%). The choice of anticoagulants at registration is detailed in Figure 1. Patients with hepatic vein thrombosis were more likely to be on anticoagulants and antiplatelets (25.8%) than those without hepatic vein thrombosis (9.4%), which was statistically significant (p = 0.004). 13 patients switched from warfarin to direct oral anticoagulant (DOAC) due to convenience, and three patients switched from DOAC to warfarin due to thrombosis.
Figure 1. Anticoagulant at registration (n = 223)*
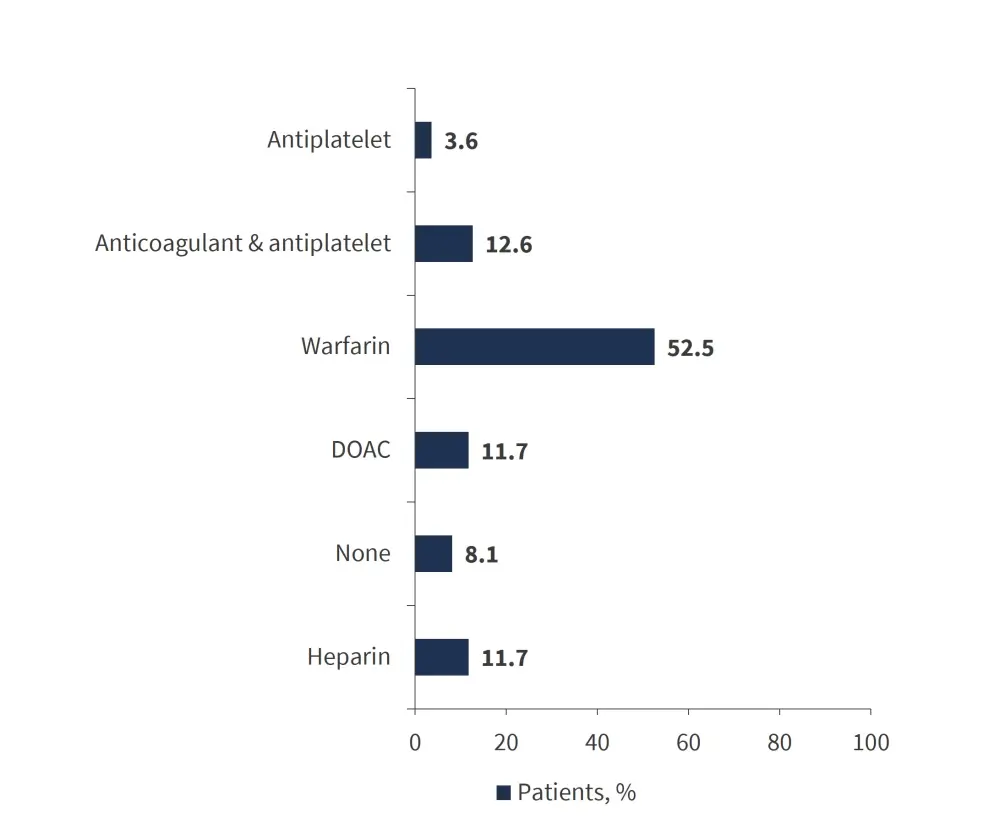
DOAC, direct oral anticoagulant.
*Adapted from Hargreaves, et al.1
Cytoreduction
153 patients (68.9%) received cytoreduction treatment on registration. The cytoreductive agent was switched in 55 patients (35.9%) due to intolerance (50.9%) and lack of response (32.7%). 10 patients (21.7%) switched from hydroxycarbamide to ruxolitinib, and six patients (13.0%) switched from hydroxycarbamide to pegylated interferon. The cytoreductive agents used at registration are displayed in Figure 2.
Figure 2. Cytoreductive agents at registration (n = 153)*
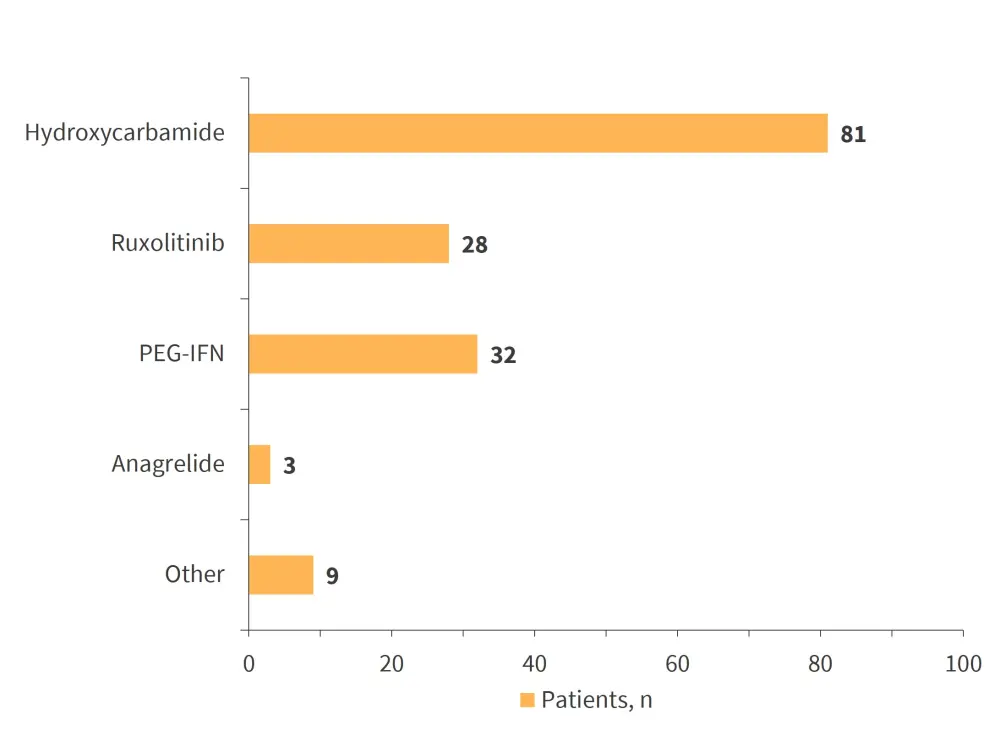
PEG-IFN, pegylated interferon.
*Adapted from Hargreaves, et al.1
Interventions
Interventions included radiological, surgical, and hematologic procedures in 203 patients.
- A transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt insertion was performed in 44 patients (21.7%), of which 70.4% had hepatic vein thrombosis (p < 0.0001). Three patients (1.5%) had venoplasty, and two patients (1.0%) had directed thrombolysis.
- Three patients underwent allogeneic stem cell transplantation: post-PV-myelofibrosis (n = 2), and MPN/myelodysplastic syndromes (n = 1).
Surgical interventions were needed in 52 patients (25.6%) and are detailed in Figure 3.
Figure 3. Surgical procedures performed in 52 patients*
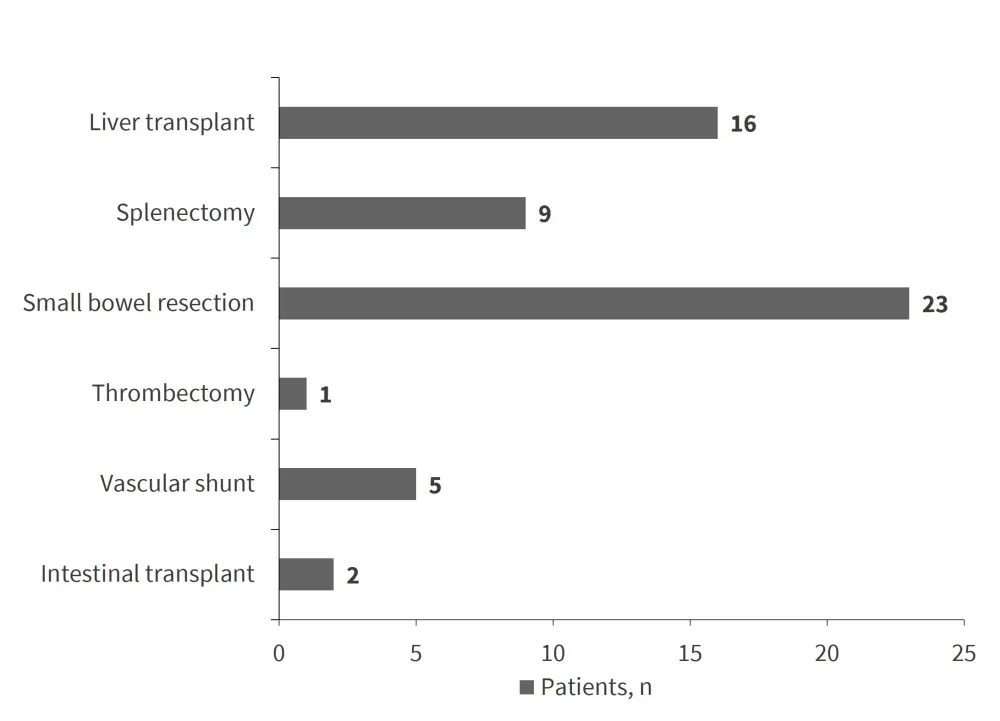
*Adapted from Hargreaves, et al.1
Additional thrombotic events
In addition to SVT, 35% of patients experienced an arterial (9.9%) or venous thrombotic event (25.1%; Table 1).
- In 43.4% of patients with MPN-SVT, SVT predated additional thrombosis (>1 year) despite anticoagulation.
- 27.6% of patients had concurrent SVT and thrombosis (±1 year).
A clinically significant hemorrhage occurred in 59 out of 217 patients (27.2%) who had a clinically significant hemorrhage. 28 of these patients (47.5%) had a hemorrhage within 1 year of SVT, and 10 patients had ≥3 hemorrhages. The rate of additional venous and arterial thrombosis is displayed in Table 1.
Table 1. Additional arterial and venous thrombosis*
|
DVT, deep vein thrombosis; PE, pulmonary embolism; SVT, splanchnic vein thrombosis; TIPSS, transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt. |
|
|
Thrombotic event, % |
Patients (n = 78) |
|---|---|
|
Arterial (n = 22) |
|
|
Cerebrovascular |
4.0 |
|
Cardiac |
2.2 |
|
Other |
3.6 |
|
Venous (n = 56) |
|
|
PE/DVT |
11.7 |
|
SVT recurrence |
4.9 |
|
TIPSS thrombosis |
6.8 |
|
Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis |
4.0 |
|
Other/unspecified |
4.5 |
Survival
The overall survival rate for the MASCOT cohort was 88%. 14 patients died with six of these deaths being disease-related. Three of the patients who died had hepatic vein thrombosis, and one had undergone allogeneic stem cell transplantation. The median age at death was 72, and death occurred at a median of 12 years post-SVT diagnosis.
Conclusion
MASCOT created a large, web-based, contemporary MPN-SVT cohort and provided more insight into the demographics of patients with MPN-SVT, which are similar to other studies. The study displays the level of disease burden faced by patients with MPN-SVT, with over 50% requiring surgical or radiological intervention. The level of diagnostic reclassification of MPN diagnosis was high (25%), suggesting the need for a dynamic diagnostic approach. The study showed that one-third of patients received inappropriate cytoreduction, highlighting the importance of more collaborative studies to identify patients suitable for cytoreduction. The thrombosis recurrence rate (4.9%) was greater than the rate reported for patients with non-MPN-SVT. DOACs were used in 12% of patients in this cohort; this is an evolving trend that requires further investigation in this cohort of the study. There was a high additional thrombotic rate post-SVT in this cohort, which included recurrence/extension and secondary thrombosis.
References
Please indicate your level of agreement with the following statements:
The content was clear and easy to understand
The content addressed the learning objectives
The content was relevant to my practice
I will change my clinical practice as a result of this content

