All content on this site is intended for healthcare professionals only. By acknowledging this message and accessing the information on this website you are confirming that you are a Healthcare Professional. If you are a patient or carer, please visit the MPN Advocates Network.
The mpn Hub website uses a third-party service provided by Google that dynamically translates web content. Translations are machine generated, so may not be an exact or complete translation, and the mpn Hub cannot guarantee the accuracy of translated content. The mpn and its employees will not be liable for any direct, indirect, or consequential damages (even if foreseeable) resulting from use of the Google Translate feature. For further support with Google Translate, visit Google Translate Help.
The MPN Hub is an independent medical education platform, sponsored by AOP Health, GSK, Sumitomo Pharma, and supported through educational grants from Bristol Myers Squibb and Incyte. Funders are allowed no direct influence on our content. The levels of sponsorship listed are reflective of the amount of funding given. View funders.
Now you can support HCPs in making informed decisions for their patients
Your contribution helps us continuously deliver expertly curated content to HCPs worldwide. You will also have the opportunity to make a content suggestion for consideration and receive updates on the impact contributions are making to our content.
Find out more
Create an account and access these new features:
Bookmark content to read later
Select your specific areas of interest
View MPN content recommended for you
REVEAL: Elevated WBC count and thrombotic events in PV
Between 34% and 41% of patients with polycythemia vera (PV) experience thrombotic events (TE). Established risk factors for TE include JAK2 mutation, advanced age, TE history, and elevated hematocrit.1 In addition, retrospective studies have shown elevated white blood cell (WBC) count to be associated with increased TE risk.1 Here, we summarize a prospective, observational study by Gerds et al.1 published in Blood which investigated association between WBC count and TE in patients with PV enrolled in the REVEAL study.1
REVEAL study design
- REVEAL (NCT02252159) investigated patients ≥18 years with PV with a history of, or a plan to undergo, allogeneic stem cell transplant (allo-HCT) within 3 months of enrollment.
- Data were collected for 6 months across centers in the US, from July 2014 to August 2016.
- Median follow-up was 44.7 months.
- A covariate Cox proportional hazards model was used to assess the association between WBC count and TE occurrence.
Key findings
- Overall, 2,271 patients with PV were included.
- Median age was 67 years, and 54.1% of patients were male.
- More patients were classed as high risk than low risk (77.9% vs 22.1%).
- Median disease duration from diagnosis was 4.1 years, and 20.1% of patients had a history of TE.
- Within the population analyzed, 4.7% experienced TEs at an incidence of 1.36/100 patient-years, and most experienced one event compared with two to five events (81.1% vs 18.9%, respectively).
- The cumulative incidence of venous TEs was higher than arterial TEs (3.13% vs 1.54%).
- The cumulative incidence of TEs occurring in patients classed as high risk was higher than patients classed as low risk (5.2% vs 2.78%).
- TE occurrence was significantly associated with elevated blood counts (Table 1).
Table 1. REVEAL: Blood counts and associated TE risk*
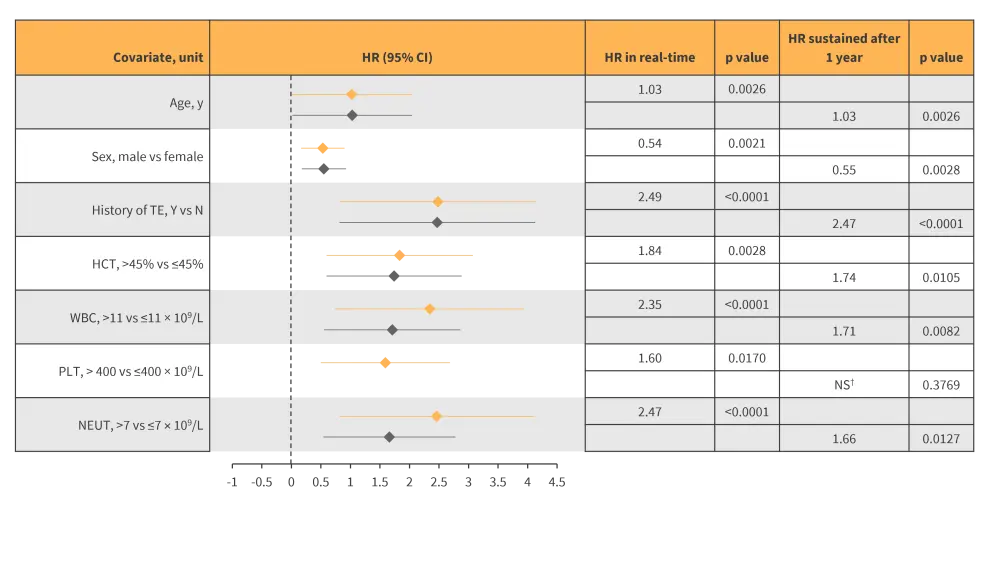
HCT, hematocrit level; HR, hazard ratio; NEUT, absolute neutrophil count; NS, not significant; PLT, platelet; TE, thrombotic event; WBC, white blood cell count.
*Adapted from Gerds, et al.1
†Association significance was not sustained a year after initial assessment.
- When comparing high-risk vs low-risk, WBC was associated with increased risk of TE in both subgroups and was the only association found in patients with low risk.
- In high-risk patients, male sex, HCT, and PLT were also associated with increased risk of TE.
|
Key learnings |
|---|
|
References
Please indicate your level of agreement with the following statements:
The content was clear and easy to understand
The content addressed the learning objectives
The content was relevant to my practice
I will change my clinical practice as a result of this content


