All content on this site is intended for healthcare professionals only. By acknowledging this message and accessing the information on this website you are confirming that you are a Healthcare Professional. If you are a patient or carer, please visit the MPN Advocates Network.
The mpn Hub website uses a third-party service provided by Google that dynamically translates web content. Translations are machine generated, so may not be an exact or complete translation, and the mpn Hub cannot guarantee the accuracy of translated content. The mpn and its employees will not be liable for any direct, indirect, or consequential damages (even if foreseeable) resulting from use of the Google Translate feature. For further support with Google Translate, visit Google Translate Help.
The MPN Hub is an independent medical education platform, sponsored by AOP Health, GSK, Sumitomo Pharma, and supported through educational grants from Bristol Myers Squibb and Incyte. Funders are allowed no direct influence on our content. The levels of sponsorship listed are reflective of the amount of funding given. View funders.
Now you can support HCPs in making informed decisions for their patients
Your contribution helps us continuously deliver expertly curated content to HCPs worldwide. You will also have the opportunity to make a content suggestion for consideration and receive updates on the impact contributions are making to our content.
Find out more
Create an account and access these new features:
Bookmark content to read later
Select your specific areas of interest
View MPN content recommended for you
DALIAH final analysis: Pegylated IFNα-2 vs hydroxyurea
Do you know... IFN treatment has disease modification potential. What percentage of patients treated with pegylated IFNα-2 experienced an absolute change in JAK2V617F allele burden from baseline to month 60?
Hydroxyurea (HU) is the most commonly used cytoreductive therapy in patients diagnosed with myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPN); however, treatment presents leukemogenic potential. Pegylated interferon alfa-2 (pegIFNα-2) offers an alternative therapeutic approach, with high response rates and disease modification potential. Each treatment presents its advantages and disadvantages; therefore, the phase III DALIAH trial (NCT01387763) was conducted to compare low-dose pegIFNα-2 with HU in patients diagnosed with MPN.
During the 65th American Society of Hematology (ASH) Annual Meeting and Exposition, Knudsen presented a final analysis of the phase III DALIAH trial. We summarize the key results below.
Check out our top abstracts, presented at the 65th ASH Annual Meeting and Exposition, here. For more information on the DALIAH trial and the quality of life outcomes experienced by patients who were enrolled, read our previous MPN Hub article.
Study design1
- The primary objective of the study was a comparison of molecular response rates at 18, 36, and 60 months
- Secondary objectives included complete clinic-hematologic response, bone marrow response, and treatment discontinuation rate
- The final analysis took place after 60 months of treatment
- The full study design has been previously reported in this MPN Hub article
Results1
The baseline patient characteristics are shown in Table 1.
Table 1. Baseline patient characteristics*
|
ET, essential thrombocythemia; HU, hydroxyurea; IFN, interferon; pegIFN, pegylated interferon; PMF, primary myelofibrosis; PV, polycythemia vera. |
||||
|
Characteristic,% (unless otherwise specified) |
HU |
IFN combined |
Total |
p value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Median age, years |
68 |
59 |
62 |
<0.0001 |
|
Male |
63 |
54 |
56 |
0.37 |
|
MPN diagnosis |
||||
|
ET |
39 |
24 |
36 |
0.09 |
|
PV |
41 |
55 |
44 |
0.15 |
|
Pre-PMF |
9 |
3 |
8 |
0.32 |
|
PMF |
11 |
18 |
12 |
0.27 |
|
IFN treatment type |
||||
|
pegIFNα-2a |
— |
50 |
50 |
— |
|
pegIFNα-2b |
— |
50 |
50 |
— |
|
JAK2V617F allele burden |
37 |
33 |
34 |
0.78 |
Efficacy
- There were no significant differences in molecular response rates between HU and pegIFNα-2 treatment in the intent-to-treat population.
- In contrast, for patients who remained on treatment, patients on pegIFNα-2 therapy experienced superior molecular response rates vs HU at 36 months and beyond (Figure 1).
Figure 1. Patients who remained on treatment and experienced a molecular response with either HU or pegIFNα-2*
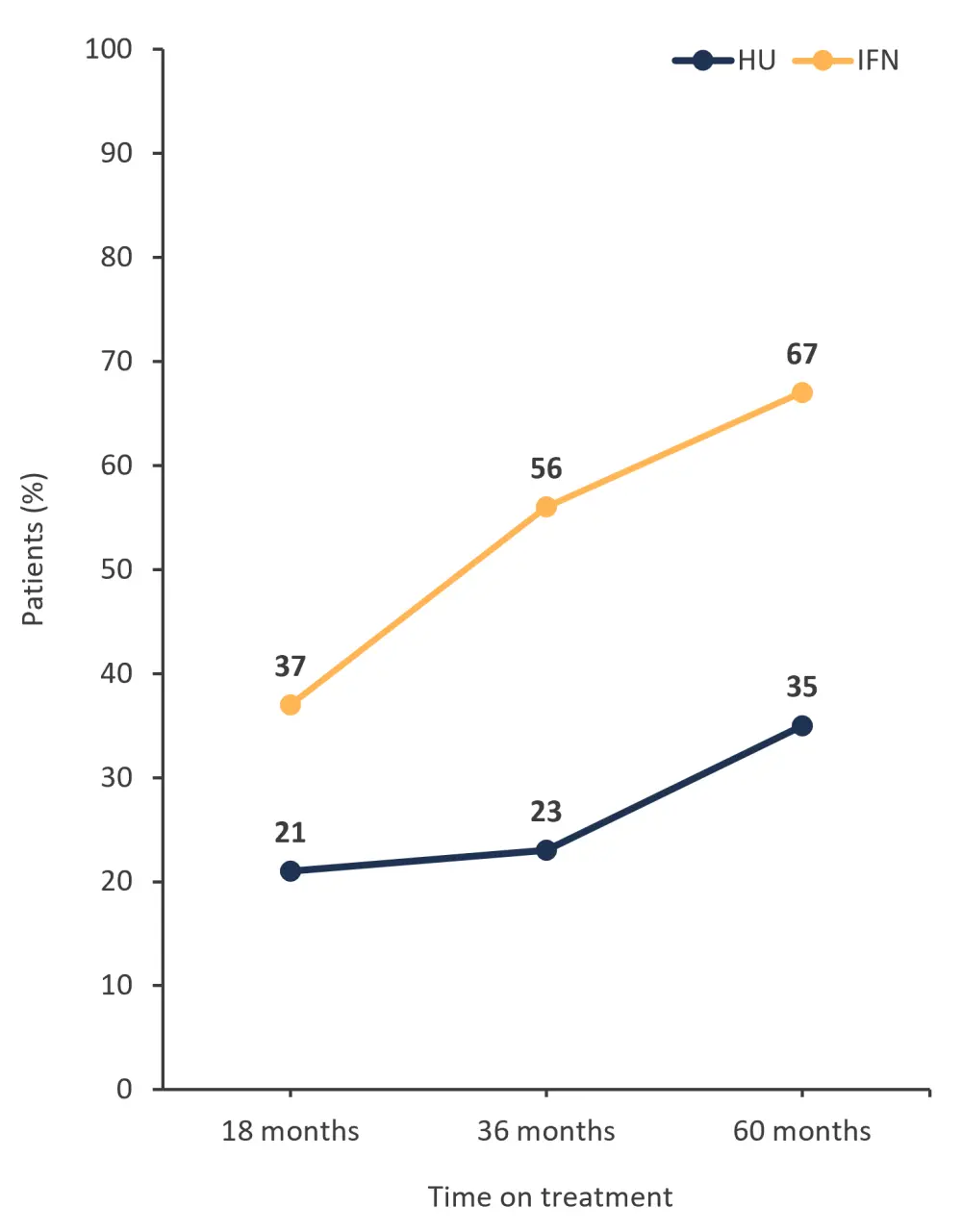
HU, hydroxyurea; IFN, interferon; pegIFNα-2, pegylated interferon alfa-2.
*Adapted from Knudsen.1
- Treatment with pegIFNα-2 resulted in a greater absolute change in JAK2V617F allele burden of 20% from baseline to Month 60, compared with a 7% absolute change with HU (p = 0.005)
- The median JAK2V617F allele burden was also lower at 36 months in patients treated with pegIFNα-2 compared with HU
- The percentage of patients who remained on treatment and experienced a complete hematologic response was higher at 36 months for pegIFNα-2 compared with HU (Figure 2)
Figure 2. Patients who remained on treatment and experienced a complete hematologic response with either HU or pegIFNα-2*
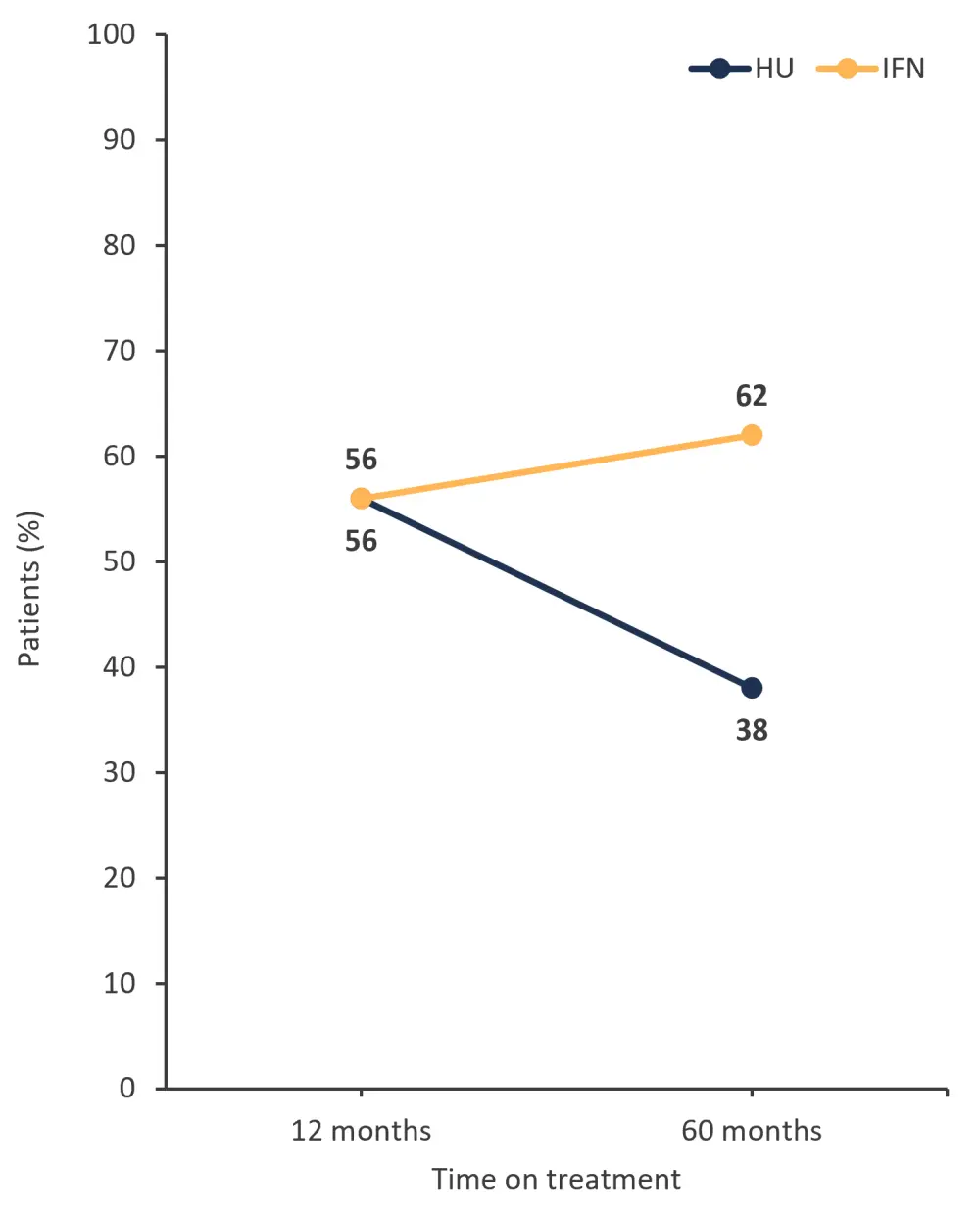
HU, hydroxyurea; IFN, interferon; pegIFNα-2, pegylated interferon alfa-2.
*Adapted from Knudsen.1
The percentage of patients who experienced no change or improvement in bone marrow fibrosis grading was similar with both pegIFNα-2 and HU treatment; however, a higher percentage of patients treated with pegIFNα-2 experienced a worsening of fibrosis (Figure 3).
Figure 3. Patients who experienced a change in bone marrow fibrosis grade, treated with pegIFNα-2 or HU*
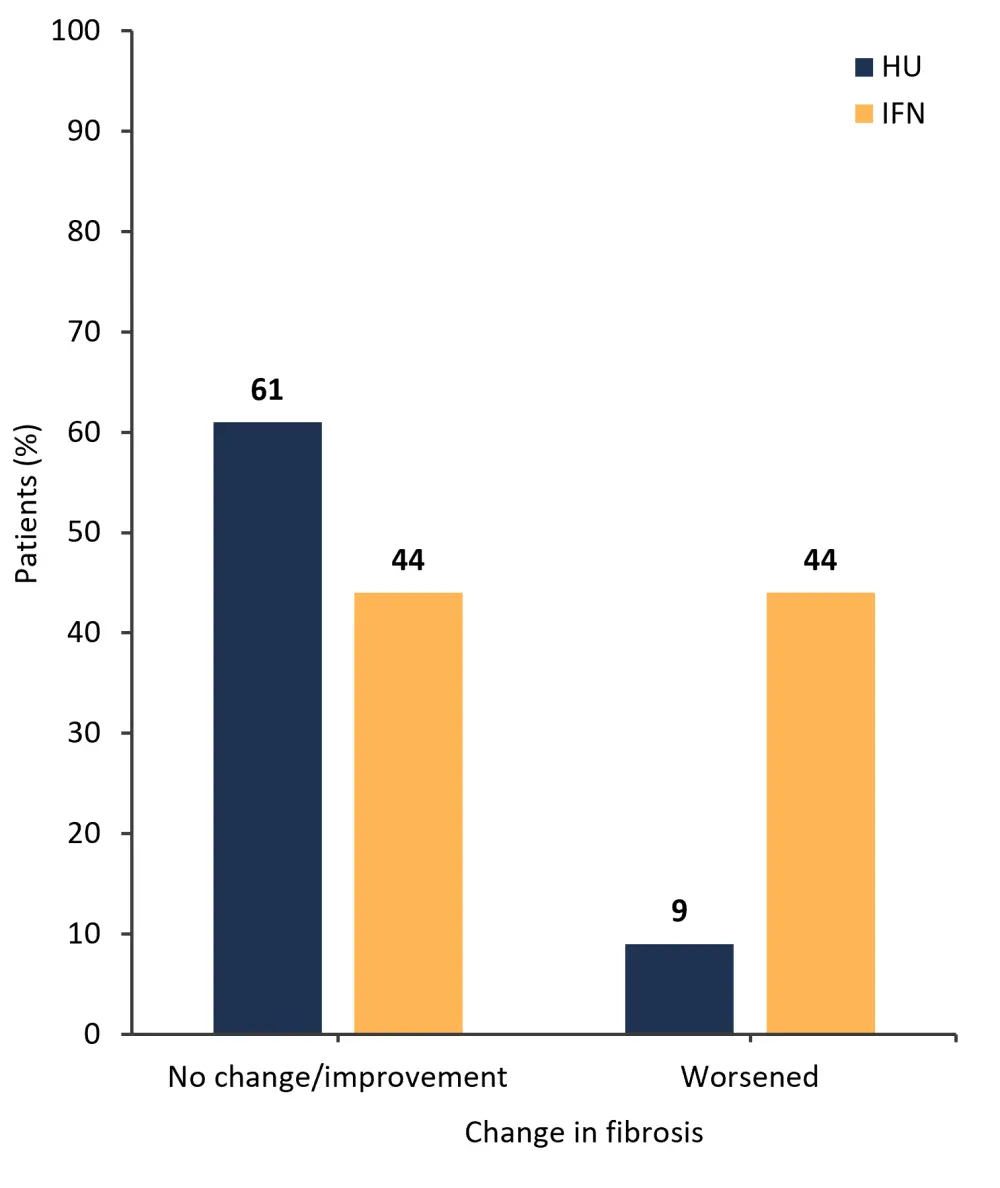
HU, hydroxyurea; IFN, interferon; pegIFNα-2, pegylated interferon alfa-2.
*Adapted from Knudsen.1
- The median duration of molecular response for patients treated with pegIFNα-2 was 36 months, compared with 28 months for HU
- Overall, 38% of patients treated with HU maintained a molecular response, compared with 9% of patients treated with pegIFNα-2 (p = 0.0002)
- The median duration of complete hematologic response for patients treated with pegIFNα-2 was 24 months, compared with 23 months for HU
- Overall, 14% of patients treated with HU maintained a molecular response, compared with 57% of patients treated with pegIFNα-2 (p < 0.0001)
Safety
- There was no difference in the frequency of any grade adverse events (AEs) for patients treated with either pegIFNα-2 or HU (99% vs 100%, respectively)
- The frequency of Grade ≥3 AEs was also similar for both pegIFNα-2 and HU (45% vs 58%, respectively)
- Patients treated with HU experienced a higher frequency of serious AEs compared with those treated with pegIFNα-2 (25% and 39%, respectively)
- In total, 65% of patients treated with pegIFNα-2 discontinued therapy, compared with 37% of patients treated with HU
Conclusion
This final analysis of the DALIAH trial showed no difference in molecular or complete hematologic response between pegIFNα-2 and HU. However, there was a greater reduction in JAK2V617F allele burden with pegIFNα-2 treatment at 36 months and beyond compared with HU. Treatment discontinuation was higher with pegIFNα-2 treatment, despite a low-dose approach. Patients with good tolerability to pegIFNα-2 therapy experienced superior efficacy beyond 36 months compared with HU.
References
Please indicate your level of agreement with the following statements:
The content was clear and easy to understand
The content addressed the learning objectives
The content was relevant to my practice
I will change my clinical practice as a result of this content




