All content on this site is intended for healthcare professionals only. By acknowledging this message and accessing the information on this website you are confirming that you are a Healthcare Professional. If you are a patient or carer, please visit the MPN Advocates Network.
The mpn Hub website uses a third-party service provided by Google that dynamically translates web content. Translations are machine generated, so may not be an exact or complete translation, and the mpn Hub cannot guarantee the accuracy of translated content. The mpn and its employees will not be liable for any direct, indirect, or consequential damages (even if foreseeable) resulting from use of the Google Translate feature. For further support with Google Translate, visit Google Translate Help.
The MPN Hub is an independent medical education platform, sponsored by AOP Health, GSK, Sumitomo Pharma, and supported through educational grants from Bristol Myers Squibb and Incyte. Funders are allowed no direct influence on our content. The levels of sponsorship listed are reflective of the amount of funding given. View funders.
Now you can support HCPs in making informed decisions for their patients
Your contribution helps us continuously deliver expertly curated content to HCPs worldwide. You will also have the opportunity to make a content suggestion for consideration and receive updates on the impact contributions are making to our content.
Find out more
Create an account and access these new features:
Bookmark content to read later
Select your specific areas of interest
View MPN content recommended for you
Selinexor + ruxolitinib in JAK-naïve patients: Long-term follow-up from the XPORT-MF-034 study
Do you know... Results from the XPORT-MF-034 trial show potential signs of disease modification. How many patients experienced a decrease in variant allele frequency ≥20%?
Myelofibrosis is a heterogeneous, progressive, and fatal disease with several unmet needs in its therapeutic management. Due to limited responses with ruxolitinib (RUX) treatment, a lack of apparent disease modification, and the challenge of treating patients with anemia/thrombocytopenia with conventional Janus kinase inhibitor (JAKi) treatment, there remains an urgent need for therapies beyond current JAKi therapy.
Selinexor, an investigational targeted oral exportin-1 inhibitor, has shown activity against both Janus kinase/signal transducers and activators of transcription and non-Janus kinase/signal transducers and activators of transcription signaling pathways. The XPORT-MF-034 trial (NCT04562389) is an ongoing phase I/III study investigating the combination of selinexor plus RUX for the treatment of JAKi naïve patients with myelofibrosis. During the 65th American Society of Hematology (ASH) Annual Meeting and Exposition, Tantravahi presented long-term follow-up results from the XPORT-MF-034 study. Here, we summarize the key results.
For more information on the current status of combination therapies in myeloproliferative neoplasms, check out our recent article.
Study design1
The full study design and selected inclusion criteria are shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1. Study design*
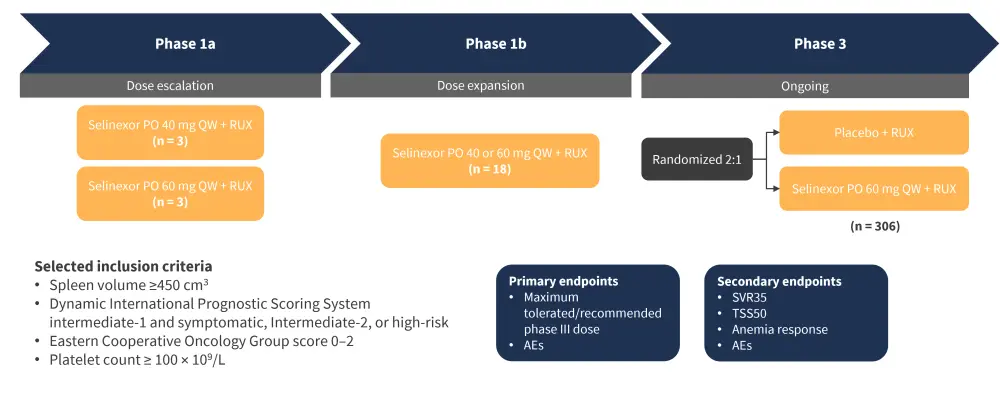
AE, adverse event; PO, oral; QW, once weekly; RUX, ruxolitinib; SVR35, spleen volume reduction ≥35%; TSS50, Total Symptom Score reduction ≥50%.
*Adapted from Tantravahi.1
Results
The baseline characteristics for patients treated with 60 mg selinexor once weekly are shown in Table 1.
Table 1. Baseline patient characteristics*
|
DIPSS, Dynamic International Prognostic Scoring System; Hb, hemoglobin; QW, once-weekly; RUX, ruxolitinib; TSS, Total Symptom Score. |
|
|
Characteristic, % (unless otherwise stated) |
Selinexor 60 mg QW + RUX |
|---|---|
|
Median age, years |
64.5 |
|
female |
35.7 |
|
Transfusion status |
|
|
Dependent |
7.1 |
|
Independent |
92.9 |
|
DIPSS risk |
|
|
Intermediate-1 |
21.4 |
|
Intermediate-2 |
57.1 |
|
High risk |
21.4 |
|
Hb level at baseline |
|
|
<10 g/dL |
57.1 |
|
≥10 g/dL |
42.9 |
|
Platelet count at baseline |
|
|
100 to <150 × 109/L |
14.3 |
|
≥150 × 109/L |
85.7 |
|
Median baseline spleen volume, cm3 |
1,961.6 |
|
Mean baseline TSS, n |
21.6 |
Efficacy
- Spleen volume reduction ≥35% (SVR35) and total symptom score reduction ≥50% (TSS50) at any time were attained by 100% and 90% of patients treated with selinexor 60 mg once weekly, respectively.
- The percentages of patients achieving SVR35 .and TSS50 at Week 12 and Week 24 are shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2. A SVR35 and B TSS50 at Week 12 and Week 24*
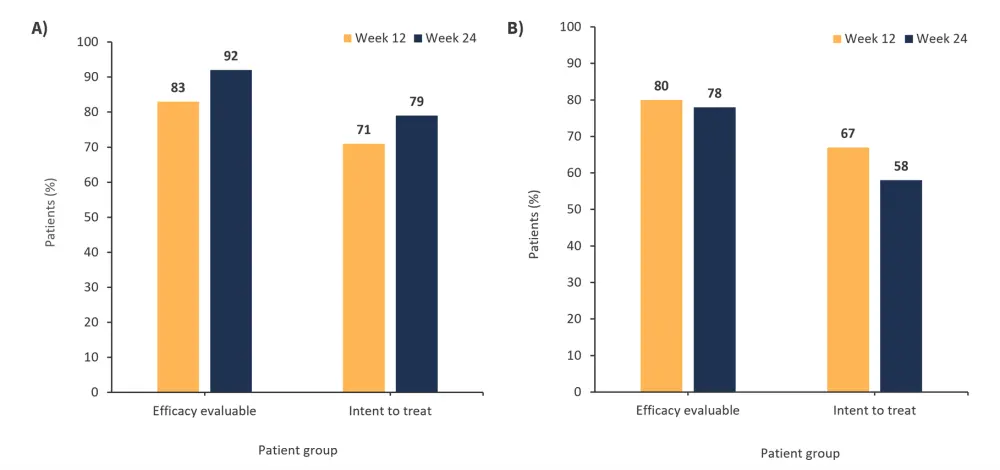
SVR35, spleen volume reduction ≥35%; TSS50, total symptom score reduction ≥50%.
*Adapted from Tantravahi.1
- The median duration of response for both SVR35 and TSS50 was not reached.
- The median time for SVR35 and TSS50 response was 12.1 weeks.
- The median duration of follow-up for SVR35 and TSS50 was 32 and 51 weeks, respectively.
- There was a 100% probability of patients maintaining SVR35 and TSS50 response.
- Patients experienced sustained decreases in proinflammatory cytokines by Week 4.
- Decreases in variant allele frequency (VAF) ≥20% were experienced by five patients.
- Three of these patients had a VAF≥ 50% at baseline.
- In total, 11 of 13 patients with VAF values at baseline achieved an SVR35 at any time.
Safety
- The most common adverse event (AE) of any grade experienced by ≥30% of patients was nausea (78.6%), followed by anemia (64.3%).
- The most common Grade ≥3 treatment-emergent AEs experienced by >5% of patients are shown in Figure 3.
- Two patients experienced treatment-emergent AEs that led to treatment discontinuation.
- Median hemoglobin and platelet counts remained stable.
- 10.1 g/dL at baseline, 9.3 g/dL at Week 12, and 10.2 g/dL at Week 24.
Figure 3. Grade ≥3 treatment-emergent adverse events experienced by >5% of patients*
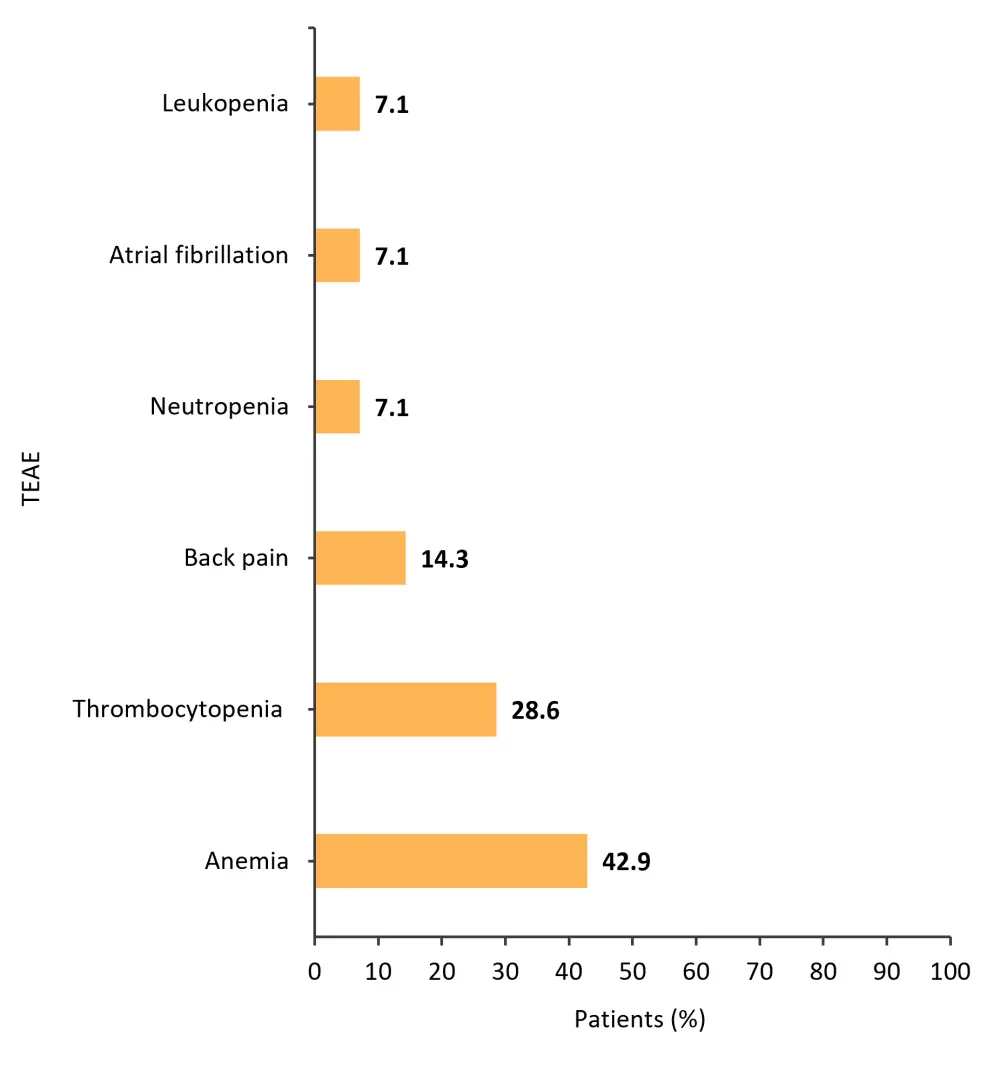
TEAE, treatment-emergent adverse event.
*Adapted from Tantravahi.1
Conclusion
This study demonstrated that selinexor and RUX was well tolerated and safety was manageable. Patients treated with selinexor 60 mg once weekly and RUX experienced durable SVR and symptom improvement, including those who received a suboptimal dose of RUX. Results also showed potential indicators of disease modification, including reduced VAF and decreased levels of proinflammatory cytokines, as early as Week 4. The combination of selinexor 60 mg once weekly and RUX has the potential to become a first-line treatment for JAKi-naïve patients with myelofibrosis and is currently being assessed in the ongoing phase III trial.
References
Please indicate your level of agreement with the following statements:
The content was clear and easy to understand
The content addressed the learning objectives
The content was relevant to my practice
I will change my clinical practice as a result of this content


